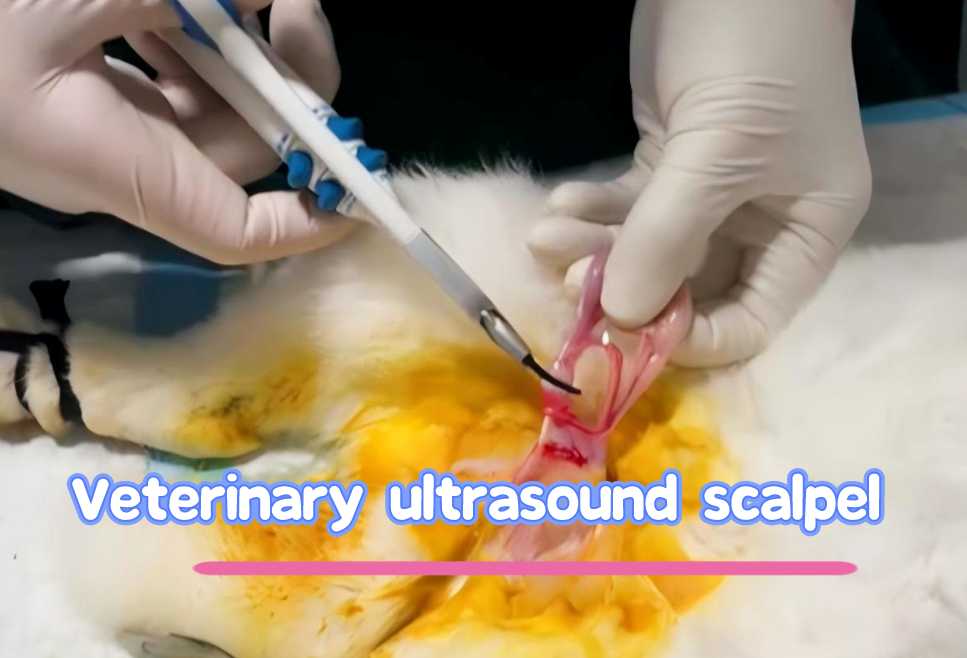
I. What is an Ultrasonic Scalpel?
The ultrasonic scalpel, formally known as an Ultrasonic Cutting and Hemostatic Device, utilizes ultrasonic cavitation effects and high-frequency mechanical vibrations to alter the structure and state of biological tissues. It is primarily used in veterinary surgery for cutting tissues and sealing blood vessels. Known as a “bloodless scalpel,” it offers advantages such as minimal bleeding, reduced damage to surrounding tissues, and faster postoperative recovery, making it a key electrosurgical tool to replace traditional mechanical scalpels.
II. Principle of Ultrasonic Scalpel Sterilization
The ultrasonic scalpel generates high-frequency vibrations, causing the blade tip to oscillate rapidly. During soft tissue cutting, these vibrations produce a low-heat effect, locally raising the temperature of the tissue. This heat activates thrombin in the tissue, triggering clotting factors and significantly shortening bleeding time.
Additionally, the cutting process creates cavitation bubbles, which help separate tissue layers, block blood vessel endings, and accelerate coagulation. This dual mechanism achieves simultaneous cutting, tissue coagulation, and hemostasis.
III. Specialized Design for Veterinary Use
Adaptation to Animal Tissue Characteristics
Adjusts vibration frequency and energy output based on the skin thickness, muscle density, and vascular distribution of different animals (e.g., dogs, cats, cattle, horses).
Diverse blade shapes (e.g., pointed, rounded, hooked) accommodate anatomical structures for procedures like abdominal surgery or hoof treatments.
Portability and Durability
Designed for diverse veterinary settings (e.g., farms, field surgeries), with lightweight, waterproof, and dust-resistant features for prolonged use.
Equipped with interchangeable blades compatible with sterilization methods (e.g., high-temperature/high-pressure or low-temperature plasma sterilization).
Safety Controls
Built-in temperature sensors prevent overheating and damage to deep tissues.
Adjustable energy output for different surgical phases (e.g., cutting vs. hemostasis).
IV. Advantages of Ultrasonic Scalpel vs. Traditional Sterilization Methods
Traditional sterilization methods typically involve surgical scalpels and sutures, which may result in longer procedure times, higher blood loss, larger incisions, and extended recovery periods.
In contrast, ultrasonic scalpel surgery offers four key advantages:
Shorter procedure time, reducing anesthesia risks.
Smaller incisions with faster healing and lower postoperative infection risks.
Rapid coagulation with near-zero bleeding and no ligation residue.
No suture rejection, leading to quicker wound recovery.
Post time: Apr-15-2025